Table of Contents
- 1 Berberine vs Metformin: A Natural Approach to Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Sensitivity
- 2 Understanding Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Sensitivity
- 3 What Is Berberine?
- 4 How Berberine Supports Blood Sugar Control
- 5 Why Metformin Is Commonly Prescribed for Type 2 Diabetes
- 6 How Metformin Works in the Body
- 7 What You Should Know About Metformin
- 8 Berberine vs Metformin: Effectiveness and Key Differences
- 9 How Moving After Meals May Help You Avoid Extra Insulin
- 10 Why I Recommend Berberine Complex
- 11 A Natural Way Forward with Berberine Complex
Berberine vs Metformin: A Natural Approach to Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Sensitivity
So often, when people hear the words “type 2 diabetes,” they immediately think of prescriptions and higher and higher doses of insulin. But that’s not the only path.
Over the years, I’ve seen so many in our community searching for natural ways to support their blood sugar, approaches that don’t just mask the problem but work with the body’s own design.
That’s where the conversation around berberine vs. metformin gets really interesting.
Both have been studied for their effects on blood sugar and insulin sensitivity, but they work in different ways.
I’ll share what I’ve learned about both and why I believe berberine deserves a place in the conversation about insulin sensitivity and wellness.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Sensitivity
Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin, the hormone responsible for moving glucose (sugar) from the bloodstream into the cells to be used as energy.
Instead of letting that sugar in, your muscle and fat cells begin to ignore insulin’s signals. This condition is known as insulin resistance.
In response, your pancreas works overtime to produce more insulin in hopes of “yelling louder” but eventually, that system wears down. You may start to feel:
- Tired all the time
- Hungrier than usual (especially for carbs)
- Noticeable weight gain around the belly
- Gradually rising blood sugar on lab work
According to a review published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, insulin resistance is a core driver of metabolic syndrome, and it’s closely tied to obesity, inflammation, and disrupted energy metabolism. The researchers explained that insulin resistance is often triggered by a mix of inactivity, excess nutrients (especially sugars), and impaired cellular signaling and may progress long before a diabetes diagnosis is made.
The good news is that there are natural ways to support insulin sensitivity, especially when changes in movement, nutrition, and supplementation are made early.
One plant-based compound that’s been getting a lot of attention in this area is berberine.
What Is Berberine?
Berberine is a plant-based compound present in herbs such as barberry, Oregon grape, and goldenseal, which have a long history of use in both Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine.
It’s not just another herbal extract; berberine has been widely researched for its potential to support metabolic health, particularly when it comes to blood sugar balance and insulin sensitivity.
Studies have shown that berberine may help activate AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase), an enzyme often referred to by researchers as a “metabolic master switch” because of its role in regulating
energy use in the body.¹
When AMPK is activated, it encourages the body to:
- Use glucose more efficiently for energy
- Reduce the amount of sugar released by the liver
- Improve insulin sensitivity in cells
- Support healthy fat metabolism
And while berberine isn’t a drug or quick fix, its ability to work with your body’s natural systems is what makes it such a promising ally in metabolic wellness.
If you’re curious to see what the science says, you can explore this study published in the journal Metabolism, which found that berberine produced a significant improvement in glucose and lipid metabolism in individuals with type 2 diabetes, results that were comparable to the commonly prescribed medication metformin.
As always, it’s not about replacing healthy habits but about supporting your body with tools that work in harmony with it.
If you want to learn more about how berberine works at the cellular level, I suggest watching this video explanation here. It breaks down the science behind berberine’s effectiveness and is based on clinical research.
How Berberine Supports Blood Sugar Control
As mentioned earlier, AMPK (adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase) is often described in research as the body’s “metabolic master switch.”
What makes berberine particularly noteworthy in the area of metabolic health is its ability to influence this enzyme. AMPK plays a central role in regulating how energy is produced and utilized. When activated, it signals cells to increase glucose uptake, reduce excessive glucose production in the liver, and enhance the breakdown of stored fats for fuel.
In a study published in Metabolism, patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes who took berberine saw significant improvements in both blood sugar and lipid metabolism, results that were found to be comparable to those taking metformin.
This means berberine may support not only healthier glucose balance but also improvements in cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which are often part of the bigger picture in metabolic health.
I also watched a great video by Dr. Liu, an infectious disease and internal medicine specialist, where she talked about berberine and its role in supporting blood sugar, metabolism, and even gut health. She explained how this natural compound may help with insulin sensitivity and calming inflammation, things that matter so much for long-term wellness.
If you want to hear it straight from her, here’s the video: No More Diabetes: The Herb That Changed Medicine
Why Metformin Is Commonly Prescribed for Type 2 Diabetes
Metformin is one of the most common prescriptions for type 2 diabetes. It’s derived from French lilac (also called goat’s rue), a plant used historically for sweet urine syndrome, an old term for diabetes.
It works by:
- Reducing how much glucose the liver makes
- Increasing insulin sensitivity
- Slowing down sugar absorption in your intestines
It’s effective, yes, but let’s talk about what’s not often mentioned.
How Metformin Works in the Body
Metformin has long been considered the first-line medication for type 2 diabetes because of how it acts on glucose metabolism.
According to a comprehensive review in the Diabetologia journal, metformin primarily works by lowering the amount of glucose produced in the liver, a process called gluconeogenesis.
It also helps the muscles and fat tissues become more sensitive to insulin, so the body can use glucose more effectively.
On top of that, metformin slows the absorption of sugar from food in the intestines, which can help blunt spikes after meals.
While these actions make metformin effective at reducing blood sugar and improving short-term control, the same review noted that its benefits are limited when it comes to addressing the root cause of type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance.
What You Should Know About Metformin
Metformin has been around for a long time and is often the first prescription given for type 2 diabetes. But as the NCBI’s StatPearls review points out, it isn’t without its drawbacks, and not everyone tolerates it the same way.
Some of the most common concerns include:
- Digestive upset – nausea, bloating, diarrhea, and stomach discomfort are among the most frequently reported side effects.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency – long-term use may reduce B12 absorption, which can affect energy, mood, and even nerve health.
- Lactic acidosis – while very rare, this serious complication is more likely in people with kidney, liver, or heart problems.
- Osteoporosis – Studies have been conducted showing Metformin’s ties to regular use and osteoporosis.
Also, the minute someone stops taking metformin, their blood sugar often goes right back up. That tells us it’s not fixing the root problem, just putting a lid on it.
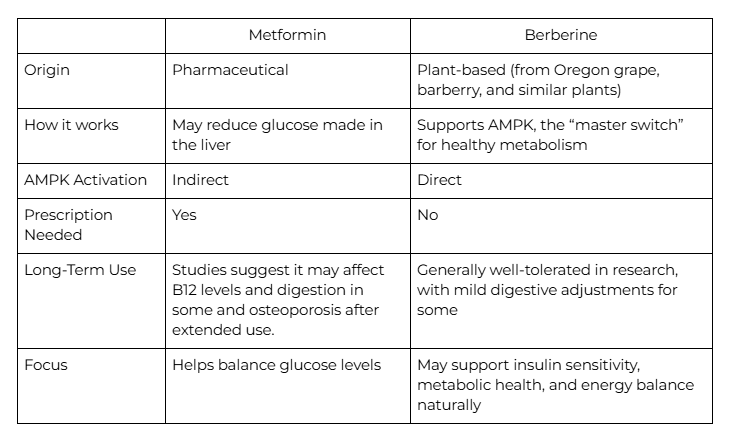
Berberine vs Metformin: Effectiveness and Key Differences
Let’s break it down in plain terms:
While both have been studied for their influence on blood sugar, what I love about berberine is how research shows it touches multiple pathways in the body, especially through AMPK activation.
For many, this means it may support not just healthy numbers, but also overall wellness, things like steady energy, metabolism, and the body’s natural balance.
How Moving After Meals May Help You Avoid Extra Insulin
This one is exciting and so simple.
When your muscles are actively contracting, they can take in glucose without the need for insulin. In other words, when you move after a meal, your body can reduce blood sugar naturally, without relying as heavily on insulin.
If you’d like to understand this better, I highly recommend this video from Glucose Goddess (Jessica Inchauspe): Move Like This After Eating (It Changes Everything) It explains in a beautifully simple way how walking, calf raises, air squats, or even vacuuming after a meal may help flatten glucose spikes and support long-term insulin sensitivity.
It’s not about running marathons or spending hours in a gym. In fact, research suggests that the timing of your movement matters just as much as the activity itself.
Starting light physical activity like walking or gentle stretching within the first 30 minutes after eating may be the most effective window to support healthy glucose levels. That’s because this is typically when blood sugar begins to rise.
Waiting too long after a meal can miss that window, since glucose may have already peaked and started its descent, making movement less impactful in managing those post-meal spikes.
Why I Recommend Berberine Complex
Whole Family Products has a long history of creating natural supplements you can trust, and our Berberine Complex is no exception.
Each capsule is made with berberine naturally extracted from Oregon grape and berries, carefully formulated to support healthy blood sugar, insulin sensitivity, and overall metabolic wellness.
What stands out to me about this formula is its broad usefulness. Many assume berberine is just for blood sugar, but its effects go well beyond that.
Alongside balanced eating and daily habits, it may help your body with insulin sensitivity, steady energy, heart and cholesterol support, gut health, and even weight management. It has also shown promise for women with PCOS by helping to regulate hormones and support metabolic health.
And here’s something I always remind our community: supplements aren’t meant to be magic on their own. But when you combine Berberine Complex with small, consistent choices, like mindful eating or a short walk after meals, it’s like giving your cells a helping hand every single day. That’s where the real difference happens.
A Natural Way Forward with Berberine Complex
Managing type 2 diabetes doesn’t have to feel like a life sentence or a narrow path with only one choice.
For so many, it’s easy to believe the only answer lies in prescriptions and higher doses of insulin, but that simply isn’t the whole picture.
God, in His wisdom, already placed what we need in creation to support our bodies (Genesis 1:29). Sometimes, it’s about going back to those gifts, leaning into nature, and pairing them with daily habits that gently guide our health in the right direction. Berberine is one of those gifts.
If you’re curious about trying berberine for yourself, our Berberine Complex at Whole Family Products was thoughtfully made with natural extracts from Oregon grape and berries. It’s one of the ways we love to support families who want to take a natural step toward better wellness.
If you’re currently on medications, check in with your holistic provider about how supplements may fit into your plan.
With small, consistent choices, you can make a meaningful difference, and we’d love to walk alongside you on that journey.